
Golf arm
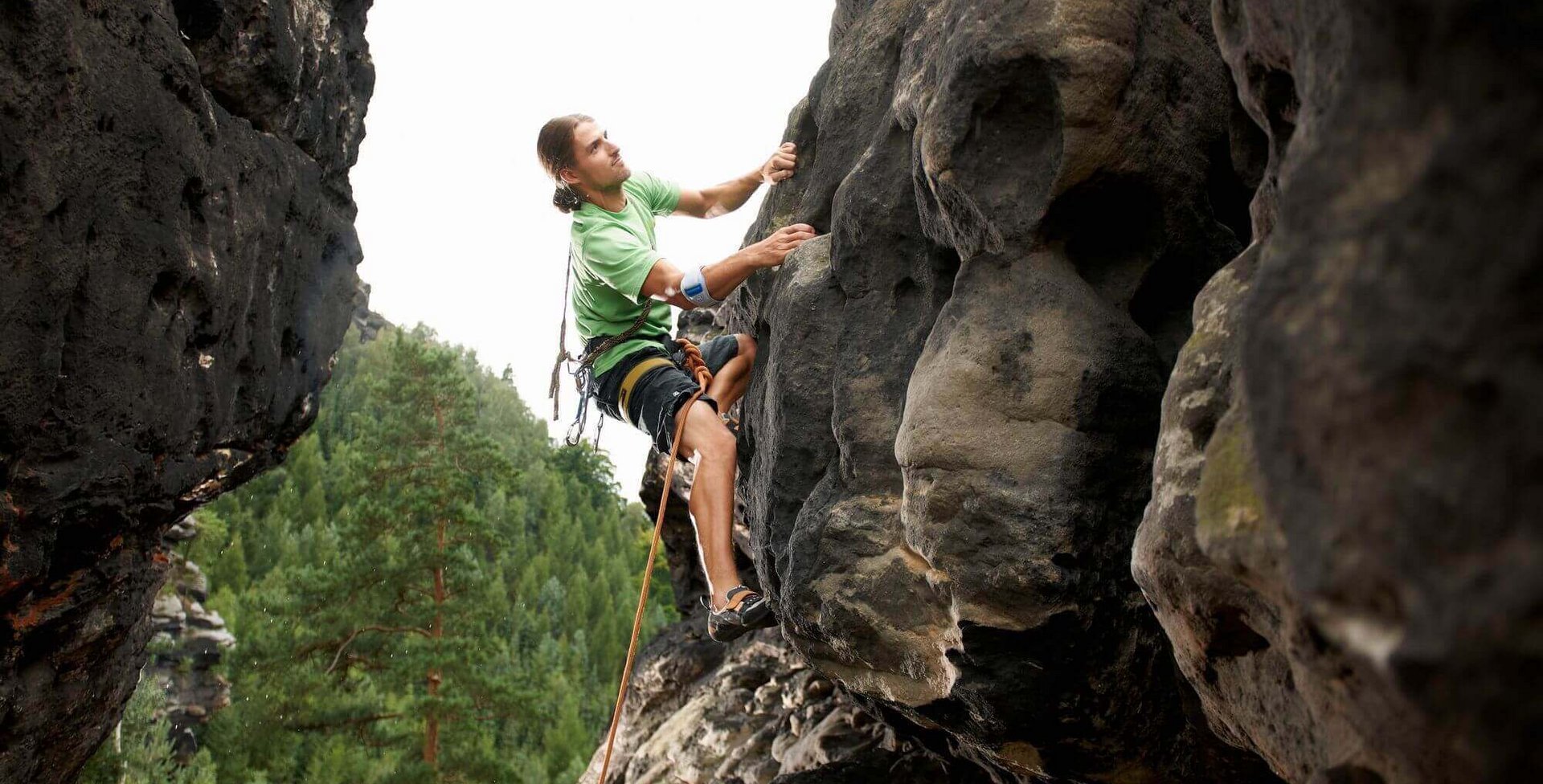
An agony that’s not just for athletes
You don’t have to be an athlete to develop golf arm. Frequent recurring strain at work and during everyday activities is often enough to cause “medial epicondylitis”, as it is known by its medically correct term. It leads to painful irritation and causes muscle insertions on the humerus to become inflamed, which is often accompanied by considerable limitations for those affected. However, the healing prospects are good if the condition is treated early, with surgery not necessary in most cases.
How does golf arm develop?
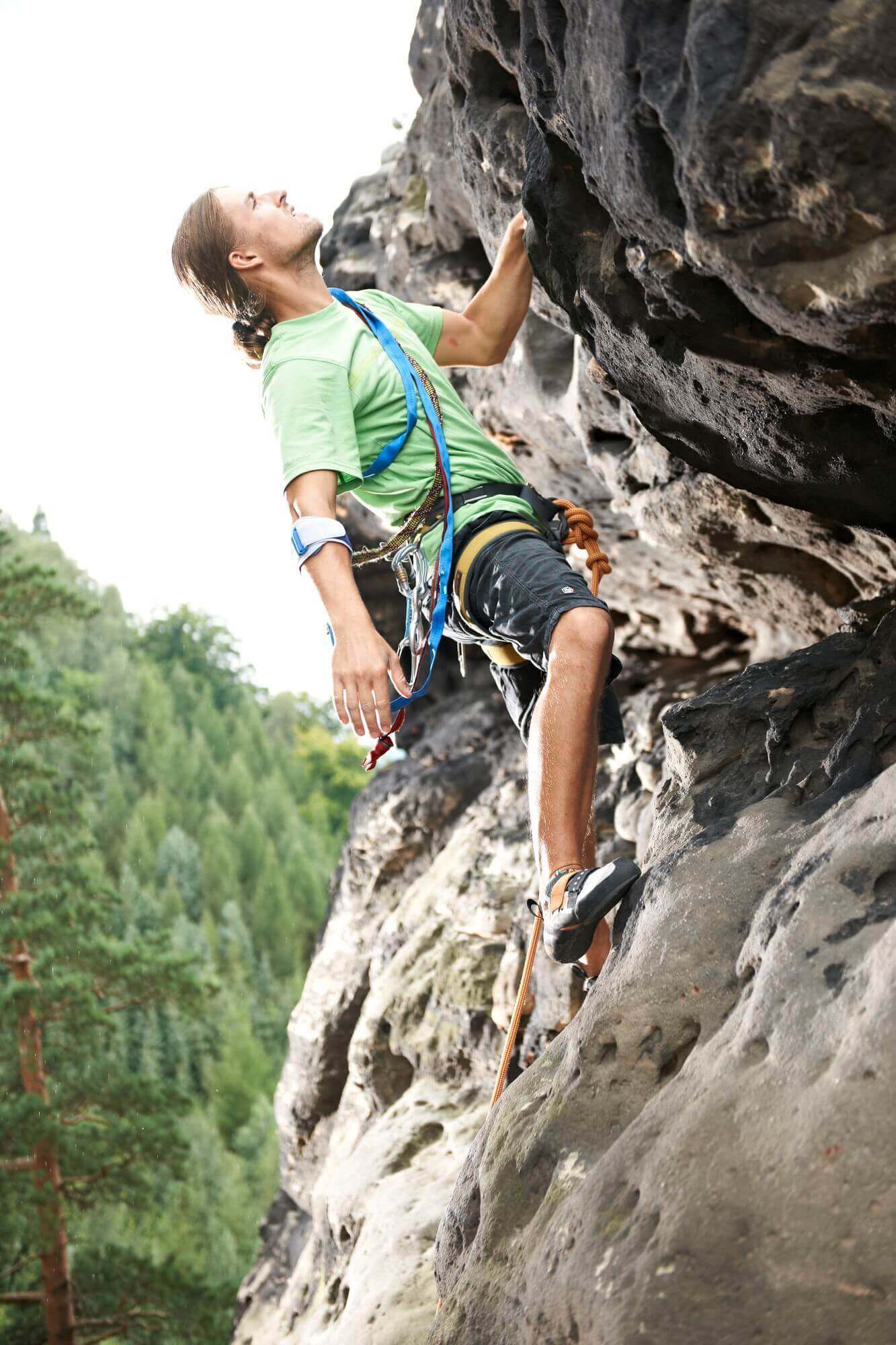

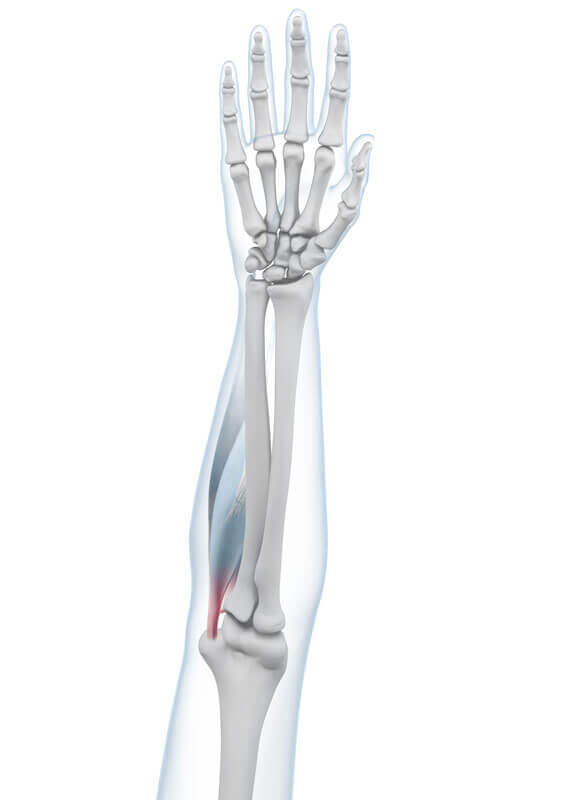
The elbow end of the humerus has two strong rounded projections (epicondyles) at which the muscles are inserted. On the inside, at the medial epicondyle, there are two long, slender muscles that extend over the elbow joint and wrist to the palm of the hand. When they are tensed, they act as flexors in both joints. A third muscle runs from the medial epicondyle to the radius, and turns the forearm inward. These three muscles together cover the major part of the epicondyle.
The tendons, which represent the transition between the muscles and the bone, are put under heavy strain during certain activities – for example, when using a screwdriver, wringing out clothes or lifting heavy objects. Even working in “forced postures” or at the computer and subjecting these muscle zones to frequently recurring jerking forces, are often not without their consequences. These occur for example when playing golf or when climbing. They cause minimal injuries (microtraumas) which tend to go unnoticed at first. In the case of golf arm, pain and inflammatory changes only develop over time when strenuous activities continue to be carried out on a regular basis.
Typical symptoms – how to identify golf arm
In the early stages of golf arm, pain initially occurs on the inside of the elbow only during activities that involve strain. This pain often subsides quickly, which is the main reason why hardly anyone affected visits a physician at this stage.
However, if this strain continues, symptoms worsen over time. Pain occurs increasingly early and lasts for longer. The affected muscle attachments are also very sensitive to pressure and feel warm, which is an unmistakable indication of inflammation. By this point at the latest, those affected should consult a physician because, if left untreated, the condition progresses and can become chronic. Furthermore, the pain is soon felt even at rest or with minimal strain, which leads to significant restrictions and makes normal use of the arm impossible. Pain radiating to the upper arm and forearm is not uncommon at this stage.
How do physicians treat golf arm?
Protecting the affected area of tissue and combatting inflammation are the main pillars for treating golf arm. Usually, in nine out of ten cases, surgery is not required because the condition responds well to conservative (non-surgical) treatment. Therefore, relief is initially necessary to allow the irritated muscle insertions to recover. This can be achieved with the use of an orthosis, for example. In mild cases, it is often enough just to protect the arm to allow it to heal. Anti-inflammatory ointments may also support treatment. A variety of methods used in the fields of physical therapy and physiotherapy can also encourage recovery:
Complete immobilization of the affected arm is however only necessary in rare cases. As has been shown, low-pain exercises and normal use of the arm in less stressful activities have a healing effect.
Why an orthosis can help with golf arm
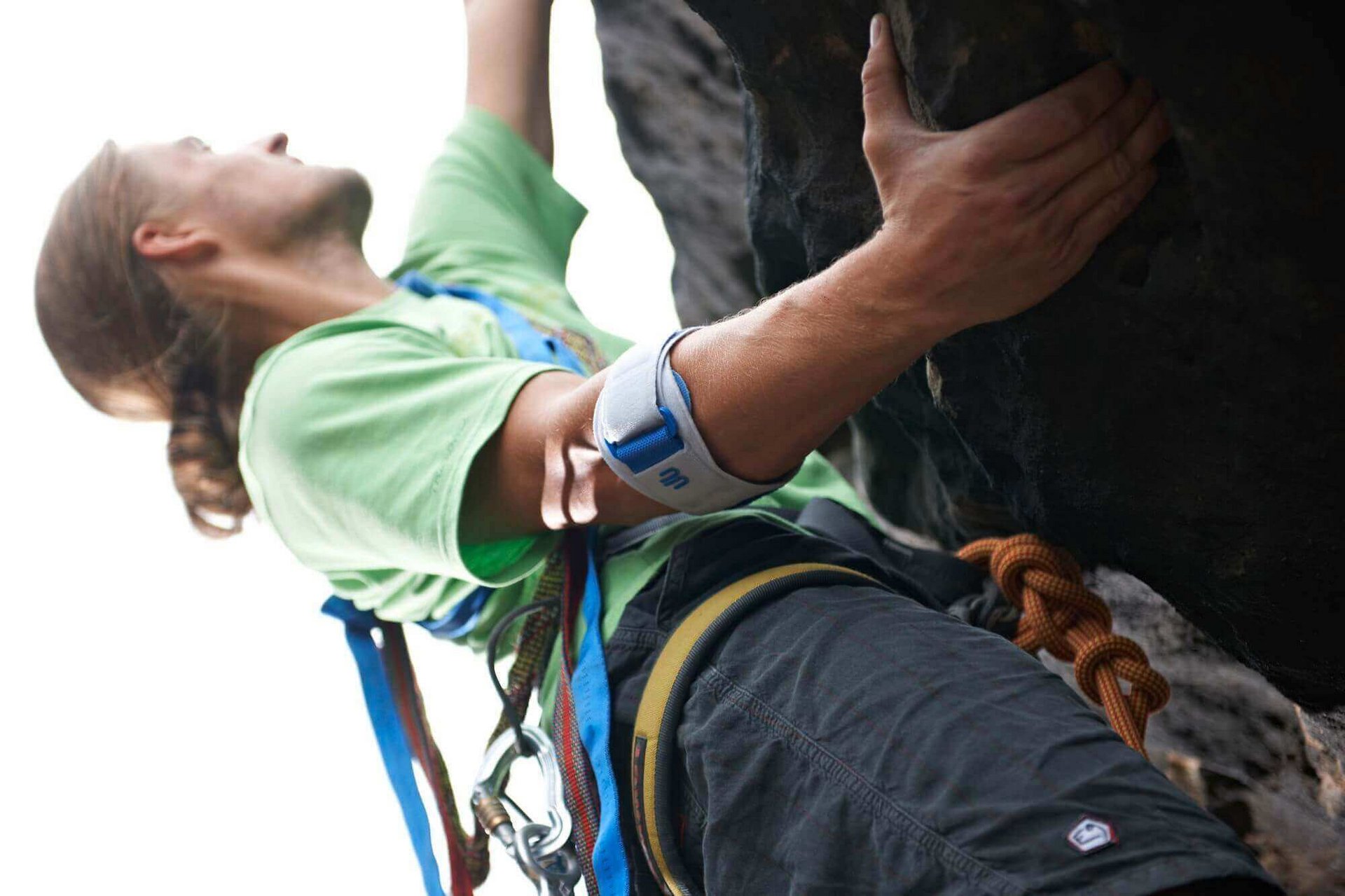

Compressive orthoses like the EpiPoint aim to reduce muscle traction on the insertion, thus reducing pain. Gentle pressure applied to the inflamed muscle insertion also promotes the reduction of inflammatory swelling (edema), relieving pressure on local nerves and blood vessels. Mobility is maintained so that the affected arm can be used in everyday pain-free activities. Cushions with nubs (pads) relieve the irritated tendon inserts precisely and provide stimulation for the injured muscle tissue. This activates the metabolism, which also promotes healing. Because the EpiPoint stabilizing orthosis is made of breathable, skin-friendly material, it also provides a high level of wearing comfort without being constrictive and prevents the affected area from overheating. The EpiPoint fits seamlessly into the overall treatment concept and perfectly supports recovery.
EpiPoint®
Pain-relieving epicondylitis brace for irritated tendon insertions
EpiPoint can be positioned either on the right or left arm using an elastic Velcro fastening. A five-point pad stimulates the painful tendon insertion on the inner or outer side of your elbow.
To product page


